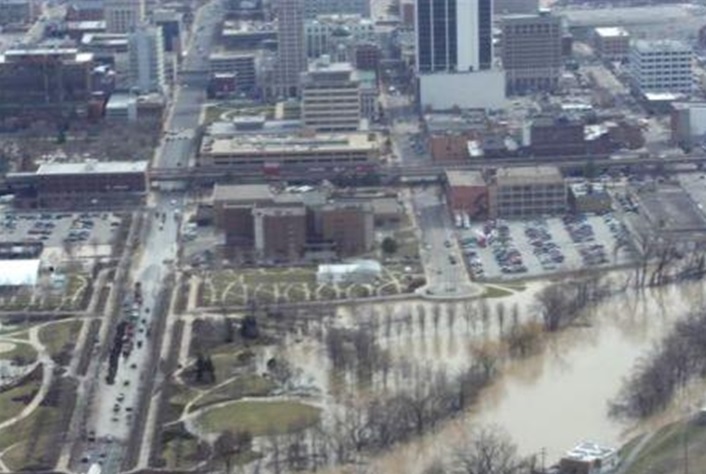
Flood Control
FLOOD CONTROL - Emergency Action Information
____________________________________________
| ESSENTIAL FLOOD PREPAREDNESS ITEMS |
|
•Glasses
|
•Sanitary & toilet supplies
|
|
•Hearing aid batteries
|
•Flashlight, batteries & bulbs
|
|
•First-aid supplies
|
•Battery-operated portable radio
|
|
•Baby formulas & supplies
|
•Shovel, hammer, pliers, axe & screwdriver
|
|
•Non-perishable foods
|
•Blankets
|
|
•Pet food
|
•Dry clothing (especially shoes & socks)
|
|
•Important papers
|
•Rubber boots, gloves & hardhat
|
|
•Bank & checkbook
|
•Valuables (jewelry, pictures, etc.)
|
|
•Water purification tablets and/or
5.25% sodium hypochlorite liquid bleach
|
•Group games
|
Below are suggestions from the Army Corps of Engineers regarding actions that should be taken before a flood to prevent or decrease damage to your home and personal property.
Radio and television stations, newspapers and police and fire department personnel provide warnings about possible flooding in low-lying areas. If you live in an area subject to flooding, it is imperative that you know the level of your property in relation to the river flooding stages. If you live below the flood level, you will have an idea of how high the water will be in your home.
In the event of a flash flood warning, immediate action is necessary to save yourself and your family. Know in advance the route you will take to avoid the flood waters, for they are unpredicatable and deadly. Flash floods are ranked in terms of whether they will be minor, moderate or severe.
If you have to evacuate your home, there are certain essential items you should take with you that can be used during or after a flood. They can be found in the list to the left. Pack these in your car to be ready to go when you do.
1.) Move as many household items as possible to the highest place possible. Place furniture on beds and personal items on the furniture. Also, items can be placed on the roof covered with polyethylene sheet stapled in place using thin strips of wood or heavy cardboard.
- Include cardboard boxes and newspapers as items to be moved to higher ground because these disintegrate and clog drains as soon as flood waters recede.
- CAUTION: Your roof or upper floor may not be able to safely support additional weight of heavy equipment or furniture so check first.
2.) Anchor, secure or weigh-down any items that may become debris or battering rams in moving water
- For example, tie furniture and personal items on top of a bed to the bed. Then anchor the bed by tying it to the house structure.
3.) Remove all wood drawers, even empty ones, from built-ins (cabinets) and furniture (dressers). Wood swells when wet and the resulting pressure between the drawers and their containers can damage wood fibers.
4) Remove light bulbs from permanently mounted fixtures below flood level. Put the light bulbs and other glass items in a plastic bag to prevent glass from shattering and spreading.
5.) Protect valuable machinery and equipment that cannot be relocated by enclosing them in waterproof covers (Figure 3-3) or by coating them with water repellent grease. This helps minimize damage and facilitates cleaning and returning them to an operational condition. If practical, consider encircling such equipment with a wall of sandbags.
6.) Relocate chemicals that react with water to give off heat or form explosives and/or toxic gases and ensure that they are in waterproof containers. This will prevent safety hazards, pollution or damage to materials in your home.
7.) Remove and dispose of perishable food items in cabinets, refrigerators and indoor trash cans or place in plastic bags or containers and seal shut. Tie shut and anchor outdoor garbage cans to minimize spread of disease and unsanitary conditions. Tie down loose items in the yard to prevent them from being carried away by flood water or battered against other items or structures.
8.) If you have a boat, move it in such a way that you can gain access to it easily during the flood.
Return to Top
Utilities
Electrical System
 The flow of electricity in your home is controlled by either plug fuses (Figure 3-1) or circuit breakers (Figure 3-2) located within a panel board mounted on the wall.
The flow of electricity in your home is controlled by either plug fuses (Figure 3-1) or circuit breakers (Figure 3-2) located within a panel board mounted on the wall.
Read below to learn how to protect your electrical system in either case of imminent flooding or normal flood preparations:
|
Imminent Flooding
1.) If flooding is imminent, REMOVE all fuses, including the one at the main switch and at the range switch.
2.) Put them in a place above anticipated flood level.
|
Normal Flood Preparations
1.) Open the panelboard door and identify what parts of the system each plug fuse or circuit breaker controls.
- These actions help minimize the danger of short circuits when the power company returns service to your home after the flood.
2.) Then, determine which lights, appliances and outlets are controlled by that fuse or circuit breaker.
- This information may be on the back of the panelboard already.
- If it isn't available, experiment by removing each fuse or switching each circuit breaker at a time to OFF.
3.) Write this information on a sheet of paper to take with you when you evacuate or put in a place above the anticipated flood water level.
4.) Replace the fuse of switch the circuit breaker back to ON.
5.) Repeat the process until the entire electrical system of your home has been checked.
• CAUTION: Some appliances contain compressors (air-conditioners, refrigerators, freezers) that may have to rest a short time (5 minutes) before being turned on again to avoid blowing the fuse or opening the circuit.
|
Gas
Close main gas valve.
- This valve is generally located on the gas piping just prior to its entry into the gas meter.
Water
1.) Close main water valve.
- This valve is usually found on the exterior wall or on the floor of the lowest level of your home where the water supply enters.
2.) Drinking water can be stored in a clean and covered bathtub or in the hot water tank.
Fuel Tanks
1.) Anchor fuel tanks to prevent them from overturning or floating.
2.) Close fuel tank valves to prevent leaks, spills and flood infiltration.
Return to Top
The Structure
Only a qualified structural engineer can tell whether your basement can cannot withstand antcipated flood-water levels.
• If a qualified structural engineer has not checked your house to determine its structural soundness or has determined your house to be structurally incapable of withstanding additional forces created by buildup of flood waters on the outside, look at the steps to allow water in basements.
• If a qualified structural engineer has determined your house to be capable of withstanding anticipated floodwater depths, look at the steps to keep water out of basements.
|
Allow Water in Basements
1.) Open all windows.
2.) Prop open all doors to the outside, to rooms and closets, and to the garage to allow water to enter unimpeded.
• Equal pressure inside and outside lessens the chance of structural damage to your home from hydrostatic pressure and prevents it from lifting off its foundation or tipping over in most cases.
3.) Use a hammer and cold chisel to knock small holes in your concrete blcok basement walls about 1-foot above ground level to allow water to fill the basement and equalize interior and exterior pressure.
• The chisel should be longer than the block is wide.
• Holes can be patched after the flood has passed.
4.) If you have time, run tap water into the basement.
• This is slower, but is the preferred method because it is cleaner.
5.) Cover glass open windows with cardboard or heavy plastic to prevent shattering and spreading.
6.) Do not obstruct the window openings, or prevent water from passing.
|
Keep Water out of Basements
1.) Close all windows and doors.
2.) Cover all windows and doors with polyethylene sheet and boards, plywood or previously-fitted closure panels.
3.) Place sandbags and/or shoveled dirt in front of doorways and more vulnerable areas of your home to keep the water away.
• Sandbags can be made with burlap or other strong material that will not dissolve in water or break when being carried.
• Sandbags can be filled with sand or dirt.
4.) If you have a sump pump, check it to make sure it is operating properly.
|
 |
A back up valve installed in the sewer line is more expensive, but will not permit the sewer to back up into your basement. A valve should be placed outside your house where it would be easier to install and maintain. A valve can be manual or automatic. |
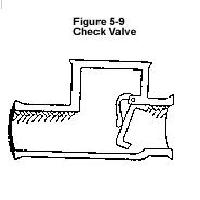 |
A check valve will permit sewage to flow outward, but not allow backflow.
• Unfortunately, a check valve requires a frequent cleaning and maintenance to remain effective which is often beyond the ability of the average homeowner.
• Consequently, the reliability of a check valve for residential use is open to question.
|
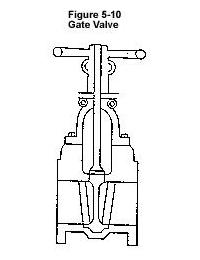 |
A gate valve is a manually operated valve which shuts off backflow and simultaneously shuts down the entire house sewer system.
• It does not require frequent cleaning and maintenance.
|
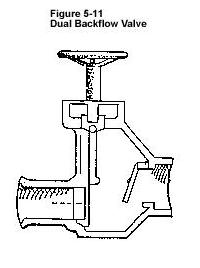 |
The dual backflow valve combines the check valve with a manually operated gate valve.
• This provides automatic check valve protection combined with the positive operation of the manual gate valve.
• This dual option may be expensive.
|
|
Plugs

|
Since the basement floor drain is the lowest point in your house, it is the first place of entry for backed-up sewers. The drain can be closed with a rubber or wooden plug during heavy rains, which is the simplest and cheapest way to stop sewer backup. Some drains are threaded for a screw-in plug.
However, the sewer could back up into the next higher opening, probably a sink drain or toilet.
• A standpipe, or a pipe inserted or screwed into the floor drain, will allow the sewer back up to seek its own level.
• This method may be more dependable than a plug that could pop out.
• However, it has the same shortcomings as a plug.
|
|
|
Overhead Sewer

|
An overhead sewer line works like a standpipe by letting water seek its own level within the pipes. Your sewer link would have to be re-built so that all house sewage drains to a pump. Sewage is then pumped up to the height of the sewer system's manhole or inlets. From there, it flows by gravity into the street before it could get high enough to back up into your house.
• This is the most expensive, but most dependable and convenient method.
|
|
|
Damage Control
While sewer back up is more common in communities with a combined sanitary and storm sewer system, sewer backup can occur when there are separate systems. Below are instructions on how to fix the 2 most common situations concerning sewer back up:
|

|
PROBLEM #1: The sewer lines on your property are broken, clogged with roots or debris or directly connected to your roof or footing drains. When heavy rain occurs, the lines cannot carry the additional water so it backs up into your basement. Tree roots can also become entangled in sewer lines, thus clogging pipes and causing sewer backups.
|
| |
SOLUTION: If this is the cause of your flooded basement, you can fix the problem relatively easily by contacting a plumber or contractor.
|
|

|
PROBLEM #2: The sewer system cannot handle the extra water during a heavy rain or flood. Because of cross connections, inadequate design, too many new houses or some other reason, the sewer mains become over loaded and back up into your basement. |
| |
SOLUTION: If this is the cause of your sewer back up, you can do one of 2 actions.
- 1.) Let the sewer back up and adjust our basement properly so it is not damaged (look at wet floodproofing section).
- 2.) Try to keep the sewer from backing up. Refer to our Prevention section.
|
It is important to know there are both advantages and disadvantages into stopping sewer back up on your own:
|
Advantages of Stopping Sewer Back Up
1.) Your basement will stay dry (assuming the flood waters do not get in through the walls or windows.)
2.) If water depths are less than a foot, they can be handled cheaply with a plug or a standpipe.
|
Disadvantages of Stopping Sewer Back Up
1.) Most methods require human intervention.
2.) Overhead sewers require a pump that needs continuous power or a back-up system in case of power failure.
3.) There will be no reduction of regular program insurance rates.
4.) If the pressure is permitted to break the sewer lines or buckle your floor, you may have a more expensive repair job than if your basement was allowed to flood.
5.) Unless you install an overhead system, you cannot use your sewers during high waters.
6.) Because the cheaper methods can cause greater pressures, costs are expensive for the most effective measures. Consult a plumber contractor.
• Check what your local ordinances say about stopping sewer build-up because it may be prohibited.
|
Pressures
If you use any of these prevention methods, you should account for two types of water pressure:
| PROBLEM #1: Your sewer pipes are probably made of clay and were not designed to operate under pressure. Once they become filled up, a valve or plug could create enough pressure to break the pipe. A standpipe or overhead sewer WILL NOT relieve this pressure. |
SOLUTION: The best way to deal with this pressure is to minimize the amount of sewer line exposed to the pressure. This could be done by installing a back up valve near your property line. Of course, this merely transfers the problem to the city. Check with your community before installing a back-up valve because some prohibit them.
|
| |
|
| PROBLEM #2: If the ground under your house becomes saturated, the water will push up on your basement floor. |
SOLUTION: The newer the sewer line, the less likely it is to leak. You may want to permit the basement to flood a little to help equalize the pressures on your floors. |
Return to Top
Appliances
 |
1.) Disconnect and store small, transportable appliances (toasters, blenders, percolators and other electrical devices) at the highest possible level (second floor or attic). If time permits, wrap these appliances and others in plastic and tie as shown in Figure 3-3.
2.) Seal openings of large appliances with wide tape such as masking or waterproof adhesive tape.
3.) Tie shut and anchor these appliances. Leave them open to allow water into the interior to prevent buoyancy.
• Top loading dishwashers and clothes washers should first be filled and weighted down with clean water to prevent buoyancy.
- Dryers can be weighted down with sandbags.
- Freezers can be weighted down with food, then sealed and anchored.
|
4.) Disconnect heavy, unmovable appliances.
- When elecrtical service is being returned after a flood, all appliances must be disconnected to determine whether any electrical problems are the fault of electrical distribution system or appliance.
- Due to water debris or wreckage, getting to electrical outlets to disconnect appliance after a flood may be difficult as well as dangerous.
5.) If time and manpower permit, remove electrical motors from washers and dryers.
- Motors from dishwashers are usually difficult to remove due to their integral attachment to the pump.
6.) Seal these motors in plastic bags and take to a higher level.
- Motors are sensitive to water and are expensive to recondition.
7.) If a sump pump is used in the basement, remove and store it in a safe, dry place above anticipated flood level.
• This will make the pump available when you return for use in pumping out any water remaining in the basement.
- If you have a second floor that is expected to stay dry, carry as many belongings as possible upstairs. However, be careful to not overload it.
8.) If flood water is expected to rise above table height on your first floor, prop open all room doors to the outside and open all windows to allow water to flow freely throughout your home.
- An equal water level inside and outside will cancel hydrostatic pressure on the walls and floors and decrease chances of major structural damage on your home.
- A house so filled with water is not likely to lift off its foundation or tip over.




 The flow of electricity in your home is controlled by either plug fuses (Figure 3-1) or circuit breakers (Figure 3-2) located within a panel board mounted on the wall.
The flow of electricity in your home is controlled by either plug fuses (Figure 3-1) or circuit breakers (Figure 3-2) located within a panel board mounted on the wall.










